1.Basic reqerment of network .
a.
NIC (Also caled lan card).
b.
Media (cable)
c.
Network devices (HUB,Switch,Router)
d.
Protocal .
e.
Logical address (IP).
2. Define Network?
A
network is a set of devices connected by physical media links. A network is
recursively is a connection of two or more nodes by a physical link or two or
more networks connected by one or more nodes.
3. What is a Link?
At the lowest level, a network can consist
of two or more computers directly connected by some physical medium such as
coaxial cable or optical fiber. Such a physical medium is called as Link.
4. What is a node?
A
network can consist of two or more computers directly connected by some physical
medium such as coaxial cable or optical fiber. Such a physical medium is called
as Links and the computer it connects is called as Nodes.
5. What is a gateway or Router?
A node
that is connected to two or more networks is commonly called as router or Gateway.
It generally forwards message from one network to another.
5. What is point-point link?
If
the physical links are limited to a pair of nodes it is said to be point-point
link.
6. What is Multiple Access?
If
the physical links are shared by more than two nodes, it is said to be Multiple
Access.
7. What are the advantages of Distributed Processing?
a.
Security/Encapsulation
b. Distributed database
c. Faster Problem solving
d. Security through redundancy
e. Collaborative Processing
b. Distributed database
c. Faster Problem solving
d. Security through redundancy
e. Collaborative Processing
8. What are the criteria necessary for an effective and
efficient network?
a. Performance
It can be measured in many ways, including transmit time and response time. b. Reliability
It is measured by frequency of failure, the time it takes a link to recover from a failure, and the network's robustness.
c. Security
Security issues includes protecting data from unauthorized access and virues.
It can be measured in many ways, including transmit time and response time. b. Reliability
It is measured by frequency of failure, the time it takes a link to recover from a failure, and the network's robustness.
c. Security
Security issues includes protecting data from unauthorized access and virues.
9. Name the factors that affect the performance of the network?
a. Number of Users
b. Type of transmission medium
c. Hardware
d. Software
b. Type of transmission medium
c. Hardware
d. Software
10. Name the factors that affect the reliability of the network?
a. Frequency of failure
b. Recovery time of a network after a failure
b. Recovery time of a network after a failure
11. Name the factors that affect the security of the network?
a. Unauthorized Access
b. Viruses
b. Viruses
12. What is Protocol?
A protocol is a set of rules that govern all aspects of
information communication.
13. What are the key elements of protocols?
The key elements of protocols are
a. Syntax
It refers to the structure or format of the data, that is the order in which they are presented.
b. Semantics
It refers to the meaning of each section of bits.
c. Timing
Timing refers to two characteristics: When data should be sent and how fast they can be sent.
a. Syntax
It refers to the structure or format of the data, that is the order in which they are presented.
b. Semantics
It refers to the meaning of each section of bits.
c. Timing
Timing refers to two characteristics: When data should be sent and how fast they can be sent.
14. What are the key design issues of a computer Network?
a. Connectivity
b. Cost-effective Resource Sharing
c. Support for common Services
d. Performance
b. Cost-effective Resource Sharing
c. Support for common Services
d. Performance
15. Define Bandwidth and Latency?
Network performance is measured in Bandwidth (throughput) and
Latency (Delay). Bandwidth of a network is given by the number of bits that can
be transmitted over the network in a certain period of time. Latency
corresponds to how long it t5akes a message to travel from one end off a
network to the other. It is strictly measured in terms of time.
16. Define Routing?
The process of determining systematically hoe to forward
messages toward the destination nodes based on its address is called routing.
17. What is a peer-peer process?
The processes on each machine that communicate at a given layer
are called peer-peer process.
18. When a switch is said to be congested?
It is possible that a switch receives packets faster than the
shared link can accommodate and stores in its memory, for an extended period of
time, then the switch will eventually run out of buffer space, and some packets
will have to be dropped and in this state is said to congested state.
19. What is semantic gap?
Defining a useful channel involves both understanding the
applications requirements and recognizing the limitations of the underlying
technology. The gap between what applications expects and what the underlying
technology can provide is called semantic gap.
20. What is Round Trip Time?
The duration of time it takes to send a message from one end of
a network to the other and back, is called RTT.
21. Define the terms Unicasting, Multiccasting and Broadcasting?
If the message is sent from a source to a single destination
node, it is called Unicasting.
If the message is sent to some subset of other nodes, it is called
Multicasting.
If the message is sent to all the m nodes in the network it is called
Broadcasting.
22. What is Multiplexing?
Multiplexing is the set of techniques that allows the
simultaneous transmission of multiple signals across a single data link.
23. Name the categories of Multiplexing?
a. Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM)
b. Time Division Multiplexing (TDM)
i. Synchronous TDM
ii. ASynchronous TDM Or Statistical TDM.
c. Wave Division Multiplexing (WDM)
b. Time Division Multiplexing (TDM)
i. Synchronous TDM
ii. ASynchronous TDM Or Statistical TDM.
c. Wave Division Multiplexing (WDM)
24. What is FDM?
FDM is an analog technique that can be applied when the
bandwidth of a link is greater than the combined bandwidths of the signals to
be transmitted.
25. What is WDM?
WDM is conceptually the same as FDM, except that the
multiplexing and demultiplexing involve light signals transmitted through fiber
optics channel.
26. What is TDM?
TDM is a digital process that can be applied when the data rate
capacity of the transmission medium is greater than the data rate required by
the sending and receiving devices.
27. What is Synchronous TDM?
In STDM, the multiplexer allocates exactly the same time slot to
each device at all times, whether or not a device has anything to transmit.
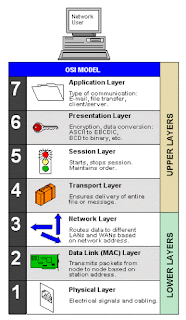
28. List the layers of OSI
a. Physical Layer b. Data Link Layer
c. Network Layerd. Transport Layer
e. Session Layer
f. Presentation Layer
g. Application Layer
29. Which layers are network support layers?
a. Physical Layer
b. Data link Layer and
c. Network Layers
b. Data link Layer and
c. Network Layers
30. Which layers are user support layers?
a. Session Layer
b. Presentation Layer and
c. Application Layer
b. Presentation Layer and
c. Application Layer
31. Which layer links the network support layers and user
support layers?
The Transport layer links the network support layers and user
support layers.
32. What are the concerns of the Physical Layer?
Physical layer coordinates the functions required to transmit a
bit stream over a physical medium.
a. Physical characteristics of interfaces and media
b. Representation of bits
c. Data rate
d. Synchronization of bits
e. Line configuration
f. Physical topology
g. Transmission mode
a. Physical characteristics of interfaces and media
b. Representation of bits
c. Data rate
d. Synchronization of bits
e. Line configuration
f. Physical topology
g. Transmission mode
33. What are the responsibilities of Data Link Layer?
The Data Link Layer transforms the physical layer, a raw
transmission facility, to a reliable link and is responsible for node-node
delivery.
a. Framing
b. Physical Addressing
c. Flow Control
d. Error Control
e. Access Control
a. Framing
b. Physical Addressing
c. Flow Control
d. Error Control
e. Access Control
34. What are the responsibilities of Network Layer?
The Network Layer is responsible for the source-to-destination
delivery of packet possibly across multiple networks (links).
a. Logical Addressing
b. Routing
a. Logical Addressing
b. Routing
35. What are the responsibilities of Transport Layer?
The Transport Layer is responsible for source-to-destination
delivery of the entire message.
a. Service-point Addressing
b. Segmentation and reassembly
c. Connection Control
d. Flow Control
e. Error Control
a. Service-point Addressing
b. Segmentation and reassembly
c. Connection Control
d. Flow Control
e. Error Control
36. What are the responsibilities of Session Layer?
The Session layer is the network dialog Controller. It
establishes, maintains and synchronizes the interaction between the
communicating systems.
a. Dialog control
b. Synchronization
a. Dialog control
b. Synchronization
37. What are the responsibilities of Presentation Layer?
The Presentation layer is concerned with the syntax and
semantics of the information exchanged between two systems.
a. Translation
b. Encryption
c. Compression
a. Translation
b. Encryption
c. Compression
38. What are the responsibilities of Application Layer?
The Application Layer enables the user, whether human or
software, to access the network. It provides user interfaces and support for
services such as e-mail, shared database management and other types of
distributed information services.
a. Network virtual Terminal
b. File transfer, access and Management (FTAM)
c. Mail services
d. Directory Services
a. Network virtual Terminal
b. File transfer, access and Management (FTAM)
c. Mail services
d. Directory Services
39. What are the two classes of hardware building blocks?
Nodes and Links.
40. What are the different link types used to build a computer
network?
a. Cables
b. Leased Lines
c. Last-Mile Links
d. Wireless Links
b. Leased Lines
c. Last-Mile Links
d. Wireless Links
41. What are the categories of Transmission media?
a. Guided Media
i. Twisted - Pair cable
1. Shielded TP
2. Unshielded TP
ii. Coaxial Cable
iii. Fiber-optic cable
b. Unguided Media
i. Terrestrial microwave
ii. Satellite Communication
i. Twisted - Pair cable
1. Shielded TP
2. Unshielded TP
ii. Coaxial Cable
iii. Fiber-optic cable
b. Unguided Media
i. Terrestrial microwave
ii. Satellite Communication
42. What are the types of errors?
a. Single-Bit error
In a single-bit error, only one bit in the data unit has changed
b. Burst Error
A Burst error means that two or more bits in the data have changed.
In a single-bit error, only one bit in the data unit has changed
b. Burst Error
A Burst error means that two or more bits in the data have changed.
43. What is Error Detection? What are its methods?
Data can be corrupted during transmission. For reliable
communication errors must be deducted and Corrected. Error Detection uses the
concept of redundancy, which means adding extra bits for detecting errors at
the destination. The common Error Detection methods are
a. Vertical Redundancy Check (VRC)
b. Longitudinal Redundancy Check (VRC)
c. Cyclic Redundancy Check (VRC)
d. Checksum
a. Vertical Redundancy Check (VRC)
b. Longitudinal Redundancy Check (VRC)
c. Cyclic Redundancy Check (VRC)
d. Checksum
44. What is Redundancy?
The concept of including extra information in the transmission
solely for the purpose of comparison. This technique is called redundancy.
45. What is VRC?
It is the most common and least expensive mechanism for Error
Detection. In VRC, a parity bit is
added to every data unit so that the total
number of 1s becomes even for even parity. It can detect all single-bit errors.
It can detect burst errors only if the total number of errors in each data unit
is odd.
46. What is LRC?
In LRC, a block of bits is divided into rows and a redundant row
of bits is added to the whole block. It can detect burst errors. If two bits in
one data unit are damaged and bits in exactly the same positions in another
data unit are also damaged, the LRC checker will not detect an error. In LRC a
redundant data unit follows n data units.
47. What is CRC?
CRC, is the most powerful of the redundancy checking techniques,
is based on binary division.
48. What is Checksum?
Checksum is used by the higher layer protocols (TCP/IP) for
error detection
49. List the steps involved in creating the checksum.
a. Divide the data into sections b. Add the sections together using 1's complement arithmetic
c. Take the complement of the final sum, this is the checksum.
50. What are the Data link protocols?
Data link protocols are sets of specifications used to implement
the data link layer. The categories of Data Link protocols are
1. Asynchronous
Protocols
2. Synchronous Protocols a. Character Oriented Protocols
2. Synchronous Protocols a. Character Oriented Protocols
b. Bit Oriented protocols
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
hello Friends
ReplyDelete